Understand How Medicare Works
Medicare Overview Chart
History of Medicare
In 1965, Congress created Medicare under Title XVIII of the Social Security Act to provide health coverage to people age 65 and older, regardless of income or medical history.
In 1972, Congress expanded Medicare eligibility to younger people who have permanent disabilities and receive Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) payments and those who have end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
In 2001 Congress expanded Medicare to cover younger people with ALS, or Lou Gehrig’s disease. Medicare originally consisted exclusively of Part A, which covers hospital and other inpatient services, and Part B, which covers outpatient care, physician visits, and other “medically necessary services”.
Today Part A & Part B combined are referred to as “Original Medicare”. Congress, under the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, created Medicare Part C (commonly called Medicare Advantage plans), which allows enrollees to receive their Medicare benefits through a private plan, while Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug plans) was created under the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003.
Medicare Benefits and Costs
Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance)
• Helps cover inpatient hospital care
• Helps cover skilled nursing facility, hospice and home health care
• Out-of-pocket costs:
o For most individuals there are no premiums for Part A coverage.
o A deductible of $1,632 (in 2024) per visit for a hospital stay of 1–60 days.
o A $408 per day co-pay (in 2024) for days 61-90 of a hospital stay.
o A $816 per day co-pay (in 2024) for days 91-150 of a hospital stay
o All costs for each day beyond 150 days
o Coinsurance for a Skilled Nursing Facility is $204 per day (in 2024) for days 21 -1000 for each benefit period.
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance)
• Helps cover doctors’ services, hospital outpatient care and home health care
• Helps cover many preventive services to help maintain your health and to keep certain illnesses from getting worse.
• Out-of-Pocket costs:
o Yearly deductible of $240.00 (for 2024)
o Coinsurance of 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for all services
o Premium varies with income:
File Individual Tax Return File Joint Tax Return Monthly Premium in 2024
$103,000 or Below $206,000 or Below $174.70*
$103,001-$129,000 $206,001-$258,000 $244.60*
$129,001-$161,000 $258,001-$322,000 $349.40*
$161,001-$193,000 $322,001-$386,000 $454.20*
$193,001-$500,000 $386,001-$750,000 $559.00*
$500,001 or more $750,001 or more $594.00*
*There is a lifetime penalty of 10% per year imposed for not enrolling in Part B unless you have proof of credible coverage
for years after you are eligible.
Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage Plans)
• Most commonly HMO of PPO plans
• Run by Medicare-approved private insurance companies
• Include Part A, Part B and usually other coverage like prescription drug coverage, sometimes for an extra cost.
• Out-of-Pocket costs:
o Part B premium must still be paid (see chart above)
o Although many are advertised as $0 additional premium plans, details vary by plan and benefits.
Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage)
• Run by Medicare-approved private insurance companies
• Helps cover the cost of prescription drugs
• Out-of-Pocket costs:
o Vary by company and formulary
o Extra Help may be available, call the Social Security Administration at 1-800-772-1213 to see if you qualify.
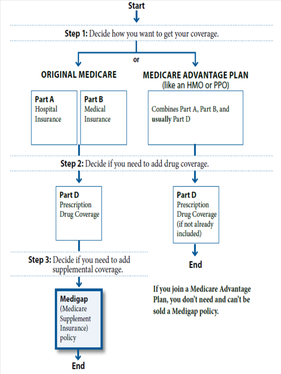
Your Medicare coverage choices at a glance
There are two main ways to get your Medicare coverage: Original Medicare or a Medicare Advantage Plan. Investigate using the buttons above to help you decide which way to get your coverage.
In 1965, Congress created Medicare under Title XVIII of the Social Security Act to provide health coverage to people age 65 and older, regardless of income or medical history.
In 1972, Congress expanded Medicare eligibility to younger people who have permanent disabilities and receive Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) payments and those who have end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
In 2001 Congress expanded Medicare to cover younger people with ALS, or Lou Gehrig’s disease. Medicare originally consisted exclusively of Part A, which covers hospital and other inpatient services, and Part B, which covers outpatient care, physician visits, and other “medically necessary services”.
Today Part A & Part B combined are referred to as “Original Medicare”. Congress, under the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, created Medicare Part C (commonly called Medicare Advantage plans), which allows enrollees to receive their Medicare benefits through a private plan, while Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug plans) was created under the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003.
Medicare Benefits and Costs
Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance)
• Helps cover inpatient hospital care
• Helps cover skilled nursing facility, hospice and home health care
• Out-of-pocket costs:
o For most individuals there are no premiums for Part A coverage.
o A deductible of $1,632 (in 2024) per visit for a hospital stay of 1–60 days.
o A $408 per day co-pay (in 2024) for days 61-90 of a hospital stay.
o A $816 per day co-pay (in 2024) for days 91-150 of a hospital stay
o All costs for each day beyond 150 days
o Coinsurance for a Skilled Nursing Facility is $204 per day (in 2024) for days 21 -1000 for each benefit period.
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance)
• Helps cover doctors’ services, hospital outpatient care and home health care
• Helps cover many preventive services to help maintain your health and to keep certain illnesses from getting worse.
• Out-of-Pocket costs:
o Yearly deductible of $240.00 (for 2024)
o Coinsurance of 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for all services
o Premium varies with income:
File Individual Tax Return File Joint Tax Return Monthly Premium in 2024
$103,000 or Below $206,000 or Below $174.70*
$103,001-$129,000 $206,001-$258,000 $244.60*
$129,001-$161,000 $258,001-$322,000 $349.40*
$161,001-$193,000 $322,001-$386,000 $454.20*
$193,001-$500,000 $386,001-$750,000 $559.00*
$500,001 or more $750,001 or more $594.00*
*There is a lifetime penalty of 10% per year imposed for not enrolling in Part B unless you have proof of credible coverage
for years after you are eligible.
Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage Plans)
• Most commonly HMO of PPO plans
• Run by Medicare-approved private insurance companies
• Include Part A, Part B and usually other coverage like prescription drug coverage, sometimes for an extra cost.
• Out-of-Pocket costs:
o Part B premium must still be paid (see chart above)
o Although many are advertised as $0 additional premium plans, details vary by plan and benefits.
Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage)
• Run by Medicare-approved private insurance companies
• Helps cover the cost of prescription drugs
• Out-of-Pocket costs:
o Vary by company and formulary
o Extra Help may be available, call the Social Security Administration at 1-800-772-1213 to see if you qualify.
Your Medicare coverage choices at a glance
There are two main ways to get your Medicare coverage: Original Medicare or a Medicare Advantage Plan. Investigate using the buttons above to help you decide which way to get your coverage.